
sound wave travel around corners this is example of diffraction. so diffraction easily observe in sound wave. Wavelength of light less than sound wave, so diffraction is more in longer wavelength. The diffraction of sound waves involves a single medium where the bending of the sound wave takes place, and then the sound wave spreads out. The highest frequency that a healthy ear can typically hear is 2.0 × 10 4 Hz.

However, even high frequency sound waves exhibit much more diffraction under normal circumstances than do light waves that pass through the same opening. The amount of diffraction (spreading or bending of the wave) depends on the. high-frequency sound waves exhibit less diffraction than low-frequency sound waves do. for audible sound normally obstacles are opening have small dimensions so d diffractions normally observed for daily life for sound wave. Do light and sound share any properties that might cause this effect. When the wavelength is longer (roughly half the length of the object), the shadows. When the wavelength is several times smaller than the object (at left), we see a reasonably clear shadow. In the top row, the parallel wavefronts from the source strike an object. (Even subatomic particles like neutrons and electrons, which quantum mechanics says also behave like waves, experience diffraction.) It's typically seen when a wave passes through an aperture. All waves do this, including light waves, sound waves and water waves. Frequency of the audible sound range 20Hz to 20 kilohertz, speed of sound in air 332 m per second then wavelength of audible sound greater than 1.6 cm and less than 16 m. Two different geometries times two different wavelengths. Diffraction is the bending of waves around obstacles or corners. In diffraction the fringe width is directly proportional to the wavelength of the wave.
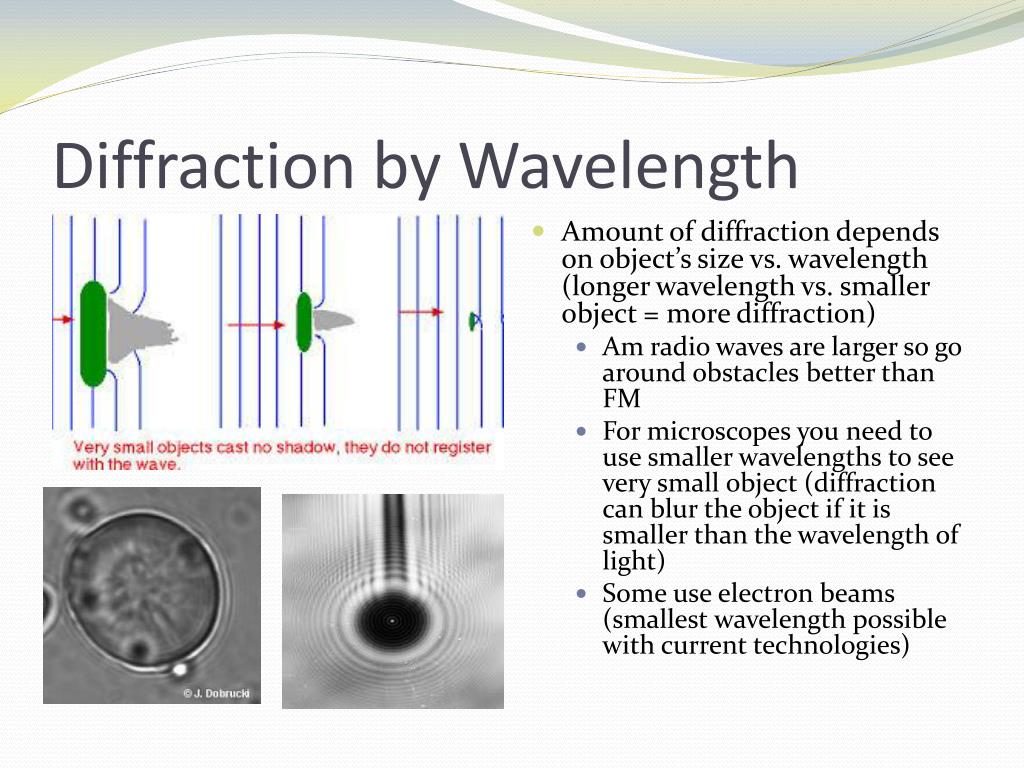
If d >wavelength diffraction effects are almost negligible if dimension of the opening obstacle greater than the wavelength of the wave. The correct option is B Wavelength of light waves is far smaller. condition: dimension of obstacle opening comparable or smaller than the wavelength of the wave, d less than or equal to wavelength. diffraction is a characteristic property of wave motion and all kinds of waves exhibit diffraction. when plane wavefront passed through a pinhole then it becomes a spherical wavefront and pinhole behave like point source. shape of wave change when meets an obstacle or opening in its path bending of the wave around the edge from an obstacle or an opening is called diffraction. Wave spread in medium or in space when wave created by vibrating source if medium is homogenous and isotropic then wavefront of point source is spherical wave, at long distance this wavefront became plane wave.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
